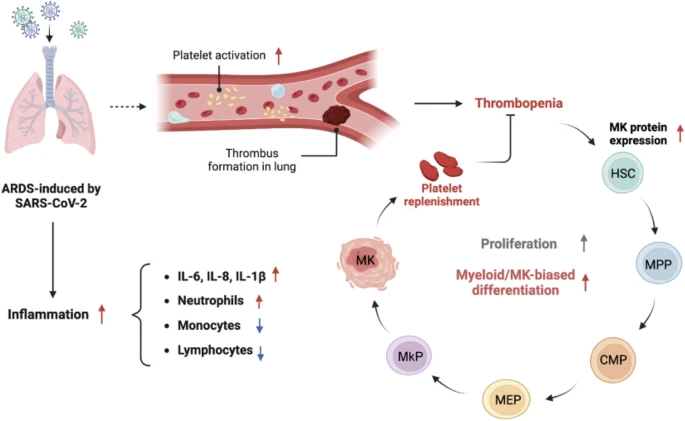
Abstract
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)-CoV-2-induced Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has caused an overwhelming influence on public health because of its high morbidity and mortality. Critical-illness cases often manifest as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Previous evidence has suggested platelets and thrombotic events as key mediators of SARS-CoV-2-associated ARDS. However, how the balance of platelet regeneration from the hematopoietic system is changed in ARDS remains elusive. Here, we reported a more severe inflammation condition and hyperactivity of platelets in COVID-19 ARDS patients compared with those infected but without ARDS. Analysis of peripheral blood revealed an increased proportion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), common myeloid progenitors (CMPs), megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors (MEPs), and megakaryocyte progenitors (MkPs) in ARDS patients, suggesting a megakaryocytic-differentiation tendency. Finally, we found altered gene expression pattern in HSCs in COVID-19 ARDS patients. Surprisingly, genes representing platelet-primed HSCs were downregulated, indicating these cells are being stimulated to differentiate. Taken together, our findings shed light on the response of the hematopoietic system to replenish platelets that were excessively consumed in COVID-19 ARDS, providing a mechanism for disease progression and further therapeutic development.
Highlights
• Hyperactivity of platelets and mild decrease in plaletlet number are observed in COVID-19 patients with ARDS.
• A more active state of the hematopoietic system is established to replenish platelet pool in COVID-19 ARDS patients.
• The influence of SARS-CoV-2 on the hematopoietic system is also manifested in altered gene expression pattern in HSC.


